AI Mouse Key Features
1. Voice Recognition and Processing:
- Accurate Speech-to-Text Conversion: Converts spoken language into text with high accuracy, supporting various accents and dialects.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Understands and processes the meaning of spoken commands and queries.
2. Voice Commands:
- Hands-Free Operation: Allows users to perform tasks and control devices using voice commands, enhancing productivity and convenience.
- Customizable Commands: Users can set up specific voice commands tailored to their workflows and needs.
3. Integration Capabilities:
- Seamless Integration: Easily integrates with existing software and hardware systems, including CRM, ERP, and other enterprise applications.
- API Access: Provides APIs for developers to create custom integrations and expand functionality.
4. Customer Interaction:
- Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: Implements voice-activated virtual assistants to handle customer inquiries and support.
- Personalized Customer Service: Delivers personalized interactions and recommendations based on customer data.
5. Accessibility and Usability:
- Multi-Language Support: Supports multiple languages, making it accessible to a global user base.
- User-Friendly Interface: Features an intuitive interface for easy setup and use.
6. Productivity Tools:
- Meeting Transcriptions: Automatically transcribes meetings and conference calls for easy reference and documentation.
- Voice-Activated Search: Enables quick and efficient searching of documents, emails, and other digital content using voice commands.
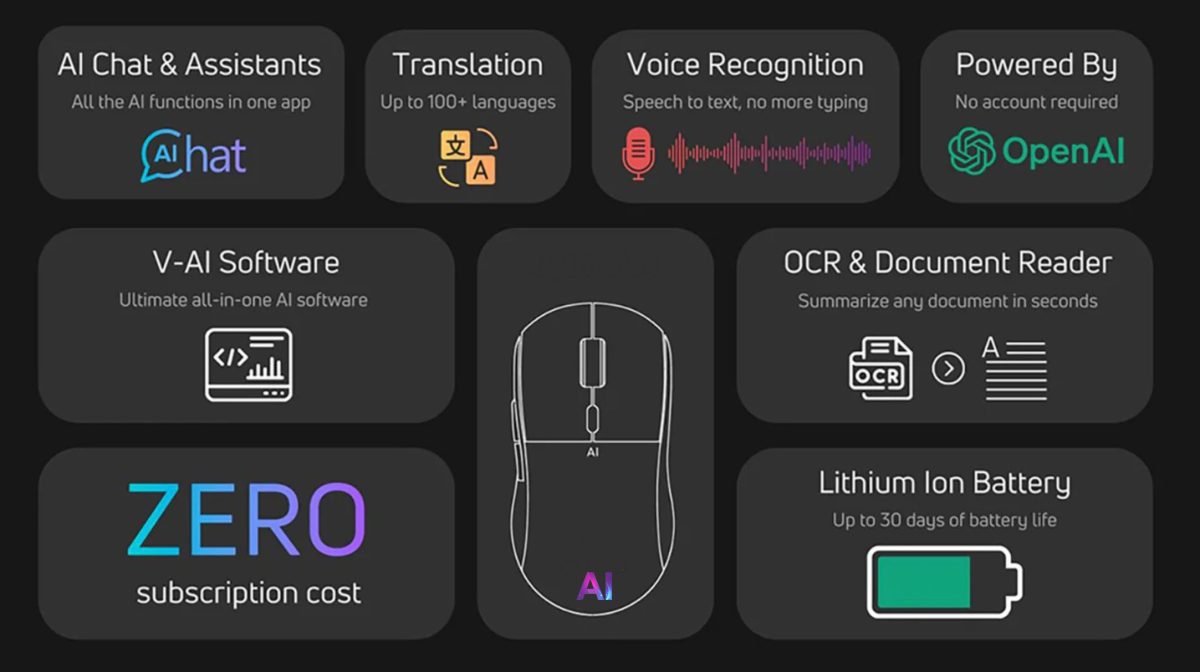
AI Mouse & NLP (Natural Language Processing)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. NLP enables machines (AI Mouse) to understand, interpret, generate, and respond to human language in a way that is both meaningful and useful.
Key components of NLP include:
1. Text Analysis:
- Tokenization: Breaking down text into smaller units such as words or phrases.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: Identifying the grammatical parts of speech in a sentence (nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc.).
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifying and classifying entities in the text (names, dates, locations, etc.).
2. Sentiment Analysis:
- Determining the emotional tone or sentiment expressed in a piece of text.
- Classifying text as positive, negative, or neutral based on the sentiment.
3. Language Generation:
- Text Generation: Creating coherent and contextually appropriate text based on input prompts.
- Summarization: Condensing longer texts into concise summaries while retaining key information.
4. Language Understanding:
- Syntax and Parsing: Analyzing the grammatical structure of sentences.
- Semantic Analysis: Understanding the meaning and context of words and sentences.
- Discourse Analysis: Understanding the context and structure of larger pieces of text, such as paragraphs and documents.
5. Machine Translation:
- Translating text from one language to another while preserving meaning and context.
6. Speech Recognition and Processing:
- Converting spoken language into text and understanding spoken commands.
- Generating spoken language from text (text-to-speech).


